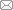
本文基于有限元模型,针对深海采矿系统悬链线立管,如图1(b),所遭遇海流、水面船运动特性,研究悬链线立管在海流和水面船运动共同影响 下的动力响应,包括水面船运动位移幅值、周期对立管等效应力和位移的影响。
图1
1 数学模型
1.1 控制方程
本文采用如下形式的结构运动控制方程
式中,$M$为质量矩阵;$K$为刚度矩阵;$F$为外载荷,如流体载荷;$X$为结构位移;$\dot{{X}}$为结构运动速度;$\ddot{{X}}$为结构运动加速度。采用有限元方法计算,隐式Newmark法求解式(1)。
采用莫里森公式计算流体载荷[13],则流体载荷$F$由两部分组成,一是由流场的速度$u$引起的黏性阻力$F_{D}$,也称为拖曳 力;二是由流场的加速度$\partial{u}/\partial{t}$引起的惯性力$F_{I}$。同时考虑结构运动的影响,则单位长度结构所受海流载荷的计算公式为
式中,$\rho_{w}$为海水密度,取值1022 kg/m$^{3}$;$u$为垂直于结构的海流流速;$C_{D}$和$C_{M}$分别为拖曳力系数和惯性力系数。$C_{A}$为附加质量力系数,满足$C_{M}=C_{A}+1$;$\partial x/\partial t$和$\partial ^2x/\partial t^2$分别为结构的运动速度和加速度。
1.2 边界条件
为了便于研究,将位于悬链线立管顶部水面船的运动简化为竖直平面内(即$xy$平面)的椭圆运动。因此,悬链线立管顶部采用随水面船运动的铰 接。悬链线立管的另一端连接自航浮体,自航浮体具有自动定位功能,保持静止状态,因此,与立管连接处采用固定铰接。
1.3 模型验证
图2
2 结果分析
2.1 材料属性及计算工况
悬链线立管物理参数如表1所示。其中,$E$为立管的弹性模量,$G$为立管的剪切模量,$\rho_{s}$为立管的密度,$D$为立管的外径,$d$为立管的内径,$L$为立管的总长。
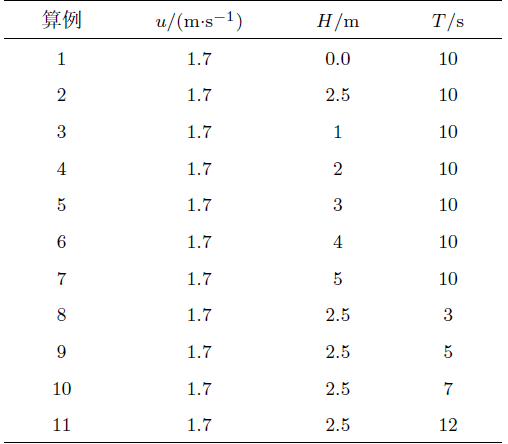
本文主要关注水面船运动特性对悬链线立管动力特性的影响,具体计算条件及参数取值列于表2,共包括11组算例。其中,$u$为海 流流速,$H$为水面船运动位移幅值,$T$为水面船运动周期。
2.2 悬链线立管形变
本文主要从悬链线立管整体变形形态、等效应力$STR$、位移$X$三方面分析悬链线立管的水动力响应及强度,其中,将整个悬链线立管上等效 应力的最大值称为最大等效应力,定义为$STR_{\max}$,将整个悬链线立管上位移的最大值称为最大位移,定义为$X_{\max}$。
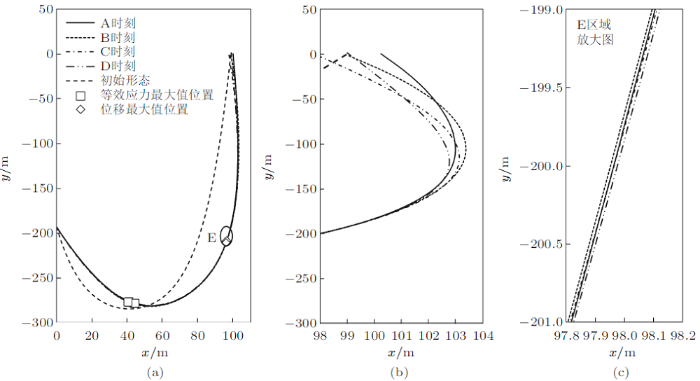
当悬链线立管在海流和水面船作用下达到动态稳定后,针对A$\sim$D四个特定时刻,即A和C时刻对应水面船水平位移最大和最小,B和D时 刻对应水面船垂向位移最大和最小,分别提取算例2条件下悬链线立管变形后的形态,并与初始形态进行对比,如图3所示。
图3
2.3 悬链线立管等效应力和位移的时间变化
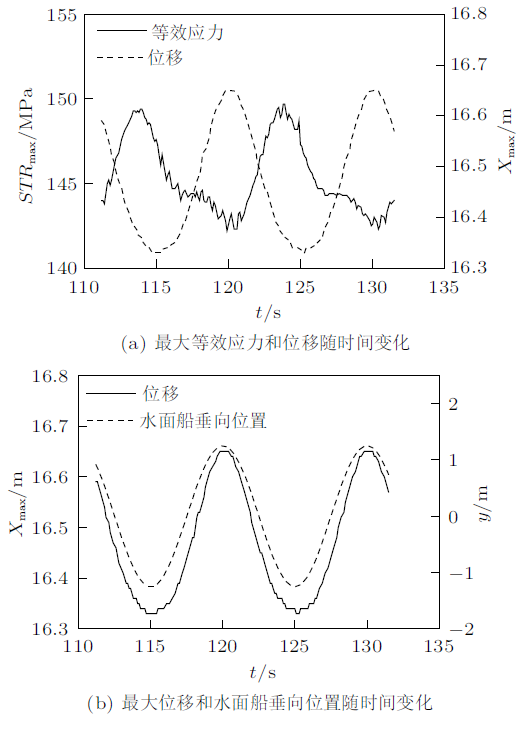
图4(a)表示算例2条件下,最大等效应力和最大位移随时间变化规律。由图可见,在水面船作周期性的椭圆运动过程中,悬链线立管的最大等 效应力和最大位移均随时间呈周期性变化,且变化周期与水面船运动周期相同,但最大等效应力和最大位移的极值点到达时间存在约$T$/2的相位差。
图4
2.4 悬链线立管等效应力和位移的空间分布
通过分析悬链线立管等效应力和位移的空间分布,得到最大等效应力和位移的分布位置,明确悬链线立管容易发生破坏之处,对工程设计具有重要意义。
图5
3 水动力响应和强度影响因素分析
本文主要分析水面船运动位移幅值$H$和周期$T$两个因素对悬链线立管动力响应的影响规律。
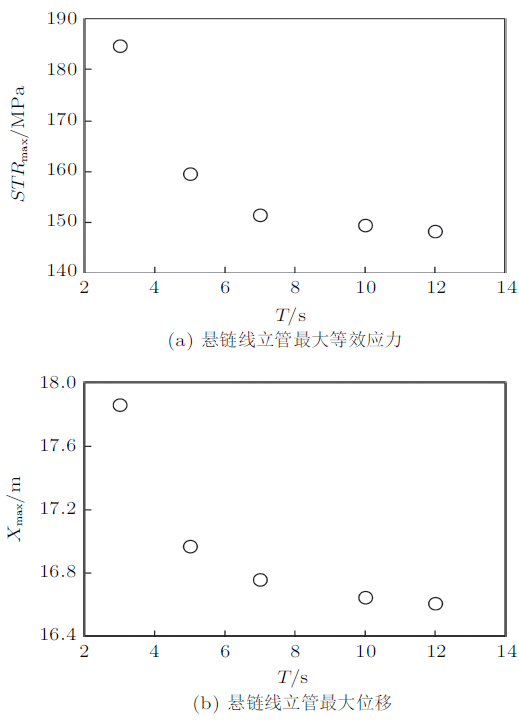
3.1 水面船位移幅值的影响
图6
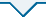
3.2 水面船运动周期的影响
图7
4 结论
以深海采矿系统悬链线立管为研究对象,同时考虑海流和水面船运动的影响,通过数值模拟的方法,研究了悬链线立管的动力响应,探讨了水面船 运动对悬链线立管的影响规律,得到以下结论:
(1) 悬链线立管最大等效应力和最大位移随时间均呈周期性变化,且存在半个周期的相位差。当水面船运动到最高点时,悬链线立管位移达到最大 值。
(2) 悬链线立管的最大等效应力和最大位移随水面船运动位移幅值的增加而增加,且增加速率逐渐增大;而悬链线立管的最大等效应力和最大位移 随水面船运动周期的增加而减小,且降低速率逐渐减小。
(3) 水面船运动位移幅值和周期对悬链线立管等效应力的影响比对其位移的影响更显著。
参考文献
一种深海采矿系统: 中国, CN206158747U
A deep-sea mining system: China, CN206158747U
Robust adaptive boundary control of a flexible marine riser with vessel dynamics
In this paper, robust adaptive boundary control for a flexible marine riser with vessel dynamics is developed to suppress the riser's vibration. To provide an accurate and concise representation of the riser's dynamic behavior, the flexible marine riser with vessel dynamics is described by a distributed parameter system with a partial differential equation (PDE) and four ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Boundary control is proposed at the top boundary of the riser based on Lyapunov's direct method to regulate the riser's vibration. Adaptive control is designed when the system parametric uncertainty exists. With the proposed robust adaptive boundary control, uniform boundedness under the ocean current disturbance can be achieved. The proposed control is implementable with actual instrumentation since all the required signals in the control can be measured by sensors or calculated by a backward difference algorithm. The state of the system is proven to converge to a small neighborhood of zero by appropriately choosing design parameters. Simulations are provided to illustrate the applicability and effectiveness of the proposed control. (C) 2011 Elsevier Ltd.
Destabilization of deep-water risers by a heaving platform
深海采矿扬矿管的横向运动响应分析
Analysis on lateral motion response of deep-sea mining riser
深海采矿扬矿管横向运动动态分析
Dynamic analysis for the lateral movement of a lifting pipe in deep sea mining
Fatigue damage of a steel catenary riser from vortex-induced vibration caused by vessel motions
A large-scale model test of a truncated steel catenary riser (SCR) was performed in an ocean basin to investigate the vortex-induced vibration (VIV) and its fatigue damage under pure top vessel motion. The top end of the test model was forced to oscillate at given vessel motion trajectories. Fiber Bragg grating (FBG) strain sensors were used to measure both in-plane and out-of-plane responses. Four different factors have been discussed to understand the VIV responses and fatigue damage results: instantaneous shedding frequency, touch down point (TDP) variation, tension variation and traveling waves. Out-of-plane VIV associated with strong time-varying features was confirmed to have occurred under pure vessel motion. Both KC number and maximum shedding frequency were investigated and indicated that the middle part of the truncated model riser was the 'power-in' region for out-of-plane VIV. Meanwhile, fatigue damage caused by out-of-plane VIV was found to be strongly dependent on both top motion amplitude and period. The probability distribution of the maximum damage exhibits 3 critical locations in the test model: TDP, upper sag-bend and top of the SCR Strong traveling waves, TOP variation and end wave reflection have been proven to cause the maximum damage locations to shift from the 'power-in' region to these three positions. Finally, a maximum fatigue damage diagram with top motion amplitude, period and maximum shedding frequency was constructed. (C) 2014 Elsevier Ltd.
Dynamic analysis of a hang-off drilling riser considering internal solitary wave and vessel motion
驳船升沉与横荡运动下的海洋立管动力响应
Dynamic response of marine risers to heave and sway of barges
Study on multimode vortex-induced vibration of deepwater riser in different flow fields by finite element simulations
Nonlinear dynamics of three-dimensional prediction model for a flexible riser under linearly sheared currents
Vessel motion effects on nonlinear dynamics of deepwater drilling riser
An experimental investigation on concomitant vortex-induced vibration and axial top-motion excitation with a long flexible cylinder in vertical configuration
The forces exerted by surface wave on piles